EXOS VM 22.6.1.4:
!!!! NOTE: Spanning Tree default changed in ExtremeXOS 22.2 !!!!
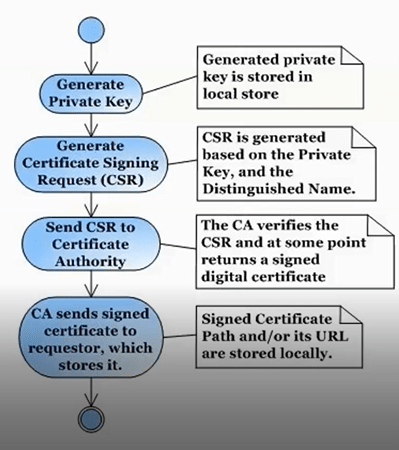
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) is enabled by default to prevent broadcast storms
Would you like to disable MSTP? [y/N/q]:
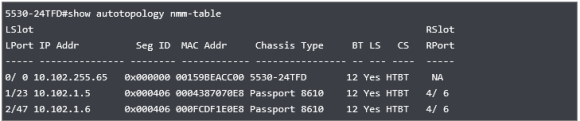
* EXOS-VM.3 # show stpd
MSTP Global Configuration:
MSTP Region Name : 0c7216bd8e00
MSTP Format Identifier : 0
MSTP Revision Level : 3
MSTP Digest : ac:36:17:7f:50:28:3c:d4:b8:38:21:d8:ab:26:de:62
Common and Internal Spanning Tree (CIST) : s0
Total Number of MST Instances (MSTI) : 0
Name Tag Flags Ports Bridge ID Designated Root Rt Port Rt Cost
s0 0000 EM—- 12 80000c7216bd8e00 80000c7216bd8e00 ——- 0
Total number of STPDs: 1 STP Flush Method: VLAN and Port
STP BPDU Forwarding: On
STP Multicast Send IGMP or MLD Query: On
Flags: (C) Topology Change, (D) Disable, (E) Enable, (R) Rapid Root Failover
(T) Topology Change Detected, (M) MSTP CIST, (I) MSTP MSTI
* EXOS-VM.5 # show stpd detail
Stpd: s0 Stp: ENABLED Number of Ports: 12
Rapid Root Failover: Disabled
Operational Mode: MSTP Default Binding Mode: 802.1D
MSTI Instance: CIST
802.1Q Tag: (none)
Ports: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,
11,12
Participating Vlans: Default
Auto-bind Vlans: Default
Bridge Priority : 32768 Bridge Priority Mode: 802.1t
Operational Bridge Priority: 32768
BridgeID : 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
Designated root : 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
CIST Root : 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
CIST Regional Root : 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
External RootPathCost : 0 Internal RootPathCost: 0
Root Port : —-
MaxAge : 20s HelloTime : 2s ForwardDelay : 15s
CfgBrMaxAge : 20s CfgBrHelloTime: 2s CfgBrForwardDelay: 15s
RemainHopCount: 20 CfgMaxHopCount: 20
Topology Change Time : 35s Hold time : 1s
Topology Change Detected : FALSE Topology Change : FALSE
Number of Topology Changes : 0
Time Since Last Topology Change: 0s
Topology Change initiated locally on Port none
Topology Change last received on Port none from none
Backup Root : Off Backup Root Activated : FALSE
Loop Protect Event Window : 180s Loop Protect Threshold : 3
New Root Trap : On Topology Change Trap : Off
Tx Hold Count : 6
Participating VLANs:
VLAN Tag Number of Ports
Ports
——————————————————————————-
Default 1 12
1(F),2(F),3(F),4(F),5(F),6(F),7(F),8(F),
9(F),10(F),11(F),12(F)
Flags: B-Blocking, D-Disabled, F-Forwarding, I-Listening, L-Learning
* EXOS-VM.6 # show stpd s0 ports
Port Mode State Cost Flags Priority Port ID Designated Bridge
1 802.1D FORWARDING 200000 eDappw–B- 128 8001 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
2 802.1D FORWARDING 200000 eDappw–B- 128 8002 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
3 802.1D FORWARDING 200000 eDappw–B- 128 8003 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
4 802.1D FORWARDING 200000 eDappw–B- 128 8004 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
5 802.1D FORWARDING 200000 eDappw–B- 128 8005 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
6 802.1D FORWARDING 200000 eDappw–B- 128 8006 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
7 802.1D FORWARDING 200000 eDappw–B- 128 8007 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
8 802.1D FORWARDING 200000 eDappw–B- 128 8008 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
9 802.1D FORWARDING 200000 eDappw–B- 128 8009 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
10 802.1D FORWARDING 200000 eDappw–B- 128 800a 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
11 802.1D FORWARDING 200000 eDappw–B- 128 800b 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
12 802.1D FORWARDING 200000 eDappw–B- 128 800c 80:00:0c:72:16:bd:8e:00
Total Ports: 12
————————- Flags: —————————-
1: e=Enable, d=Disable
2: (Port role) R=Root, D=Designated, A=Alternate, B=Backup, M=Master
3: (Config type) b=broadcast, p=point-to-point, e=edge, a=auto
4: (Oper. type) b=broadcast, p=point-to-point, e=edge
5: p=proposing, a=agree
6: (partner mode) d = 802.1d, w = 802.1w, m = mstp
7: i = edgeport inconsistency
8: S = edgeport safe guard active
s = edgeport safe guard configured but inactive
8: G = edgeport safe guard bpdu restrict active in 802.1w and mstp
g = edgeport safe guard bpdu restrict active in 802.1d
9: B = Boundary, I = Internal
10: r = restricted role, t = active role
* EXOS-VM.8 # show config stp detail
#
# Module stp configuration.
#
configure mstp region 0c7216bd8e00
configure mstp revision 3
configure mstp format 0
create stpd s0
configure stpd s0 delete vlan default ports all
configure stpd s0 mode mstp cist
configure stpd s0 forwarddelay 15
configure stpd s0 hellotime 2
configure stpd s0 maxage 20
configure stpd s0 max-hop-count 20
configure stpd s0 priority-mode dot1t
configure stpd s0 priority 32768
configure stpd s0 default-encapsulation dot1d
configure stpd s0 loop-protect event-window 180
configure stpd s0 loop-protect event-threshold 3
configure stpd s0 backup-root off
configure stpd s0 trap new-root on
configure stpd s0 trap topology-change off
configure stpd s0 trap topology-change edge-ports off
configure stpd s0 tx-hold-count 6
enable stpd s0 auto-bind vlan Default
enable stpd s0
configure stpd flush-method vlan-and-port
configure stpd bpdu-forwarding on
configure stpd multicast send-query on
After adding another EXOS switch with two inter-switch links between them forming a looped topology, the second port on the non-root bridge is BLOCKING as expected.
EXOS-VM.2 # show stpd s0 p
Port Mode State Cost Flags Priority Port ID Designated Bridge
1 802.1D FORWARDING 200000 eRapam–B- 128 8001 80:00:0c:72:16:86:e7:00
2 802.1D BLOCKING 200000 eAapam–B- 128 8002 80:00:0c:72:16:86:e7:00
 Note: This was helpful for the XP test machine I was using.
Note: This was helpful for the XP test machine I was using.