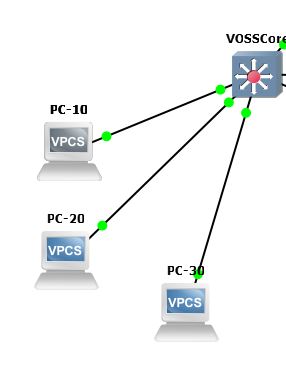
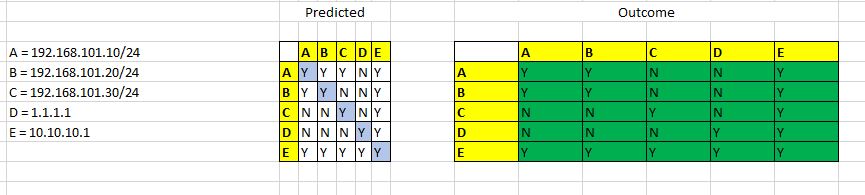
Following GNS3 simulation test to validate security ACL on VOSS. The goal is to only allow a range or specific IPs to communicate with a specific remote IP and to deny other IPs within the same VLAN subnet from communicating with other IPs inside and outside the VLAN.
# Filter Configuration
filter acl 101 type inVlan name “In vlan 101”
filter acl set 101 default-action deny
filter acl vlan 101 101
filter acl ace 101 1 name “arp req”
filter acl ace action 101 1 permit count
filter acl ace ethernet 101 1 ether-type eq arp
filter acl ace arp 101 1 operation eq arprequest
filter acl ace 101 1 enable
filter acl ace 101 2 name “arp resp”
filter acl ace action 101 2 permit count
filter acl ace ethernet 101 2 ether-type eq arp
filter acl ace arp 101 2 operation eq arpresponse
filter acl ace 101 2 enable
filter acl ace 101 3 name “192.168.101.10 to 192.168.101.20”
filter acl ace action 101 3 permit count
filter acl ace ethernet 101 3 ether-type eq ip
filter acl ace ip 101 3 src-ip eq 192.168.101.10
filter acl ace ip 101 3 dst-ip eq 192.168.101.20
filter acl ace 101 3 enable
filter acl ace 101 4 name “192.168.101.20 to 192.168.101.10”
filter acl ace action 101 4 permit count
filter acl ace ethernet 101 4 ether-type eq ip
filter acl ace ip 101 4 src-ip eq 192.168.101.20
filter acl ace ip 101 4 dst-ip eq 192.168.101.10
filter acl ace 101 4 enable
filter acl ace 101 5 name “Dst IP 10.10.10.1”
filter acl ace action 101 5 permit count
filter acl ace ethernet 101 5 ether-type eq ip
filter acl ace ip 101 5 dst-ip eq 10.10.10.1
filter acl ace 101 5 enable
filter acl ace 101 6 name “VLAN 190 Subnet”
filter acl ace action 101 6 deny count
filter acl ace ethernet 101 6 ether-type eq ip
filter acl ace ip 101 6 src-ip mask 192.168.101.0 24
filter acl ace 101 6 enable